Can two different vendor stacks pass real traffic with minimal changes and deliver production-grade services in the same network lab?
We set out to prove that OcNOS and Cisco IOS XR can work together across OSPF, Segment Routing MPLS, MP-BGP, EVPN-VPWS with clear, repeatable configurations.
Our lab used concrete configuration lines: router setup, prefix-sid values on loopbacks, and IGP-OSPF to match behavior. We enabled MP-BGP vpnv4 and EVPN between specific addresses, validated EVPN-VPWS.
Verification included show outputs, SR label allocation, EVPN route types, and ping tests between PCs to confirm data-plane reachability.
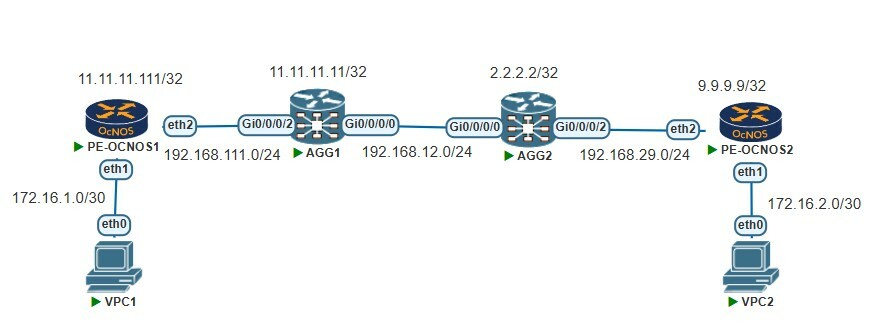
Lab Topology, Devices, and Addressing Overview
Below topology the device pairings, interface mappings, and addressing scheme that power the lab. This short description gives operators a clear starting point for repeatable tests and fast turn-up.
OcNOS OSPF + SR-MPLS configuration highlights
router ospf 1
ospf router-id 11.11.11.111
log-adjacency-changes detail
bfd all-interfaces
network 11.11.11.111/32 area 0.0.0.0
network 192.168.111.111/32 area 0.0.0.0
ospf segment-routing global block 16000 23000
segment-routing mpls
!
interface eth2
description “hacia AGG1”
ip address 192.168.111.111/24
mtu 8986
label-switching
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip ospf authentication message-digest
ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 0xb6bf08815d93bfd9
ip ospf hello-interval 10
ip ospf dead-interval 40
!
interface lo
ip address 127.0.0.1/8
ip address 11.11.11.111/32 secondary
ipv6 address ::1/128
prefix-sid index 111 no-php
IOS XR OSPF+ SR-MPLS configuration highlights
segment-routing
global-block 16000 23000
!
router ospf 1
segment-routing mpls
passive disable
address-family ipv4 unicast
area 0
interface Loopback0
passive enable
prefix-sid index 11
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0
authentication message-digest
message-digest-key 1 md5 encrypted 050E081B2440450C00
network point-to-point
segment-routing forwarding mpls
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2
authentication message-digest
message-digest-key 1 md5 encrypted 050E081B2440450C00
network point-to-point
segment-routing forwarding mpls
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2
mtu 9000
ipv4 address 192.168.111.11 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback0
ipv4 address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
!
Verification: show ospf neighbors, SR label mappings, MPLS forwarding table
OcNOS
The state of the OSPF neighbor can be confirmed by executing the show ip ospf neighbor command on the OcNOS
Check loopbacks’s SR index learning by OSPF
Display SR Index of routers in the same OSPF domain, for this example in area 0.0.0.0
IOS XR
We also verify the same on the Cisco. Note that the commands are slightly different but very similar.
MP-BGP for vpnv4 and l2vpn evpn Address Families
Now we activate MP‑BGP so L3VPN and L2VPN routes flow between our router peers.
OcNOS MBGP-L3VPN configuration and activation
ip extcommunity-list standard VPN_DATA_OLT permit rt 7922:16
!
route-map VPN_DATA_OLT_IMPORT permit 10
match extcommunity VPN_DATA_OLT
!
route-map VPN_DATA_OLT_EXPORT permit 10
match extcommunity VPN_DATA_OLT
ip vrf DATA_OLT
rd 7922:16
route-target both 7922:16
import map VPN_DATA_OLT_IMPORT
export map VPN_DATA_OLT_EXPORT
!
!
interface eth1
ip vrf forwarding DATA_OLT
ip address 172.16.1.1/30
mtu 9000
!
router bgp 7922
bgp router-id 11.11.11.111
bgp log-neighbor-changes
bgp graceful-restart
timers bgp 5 15
allocate-label all
neighbor RR_CORE peer-group
neighbor RR_CORE remote-as 7922
neighbor RR_CORE update-source lo
neighbor RR_CORE authentication-key
0xb6bf08815d93bfd9
neighbor 11.11.11.11 peer-group RR_CORE
!
address-family vpnv4 unicast
neighbor RR_CORE activate
neighbor RR_CORE next-hop-self
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf DATA_OLT
redistribute connected
exit-address-family
!
BGP VPNv4 neighbor among PE-OCNOS1 and CORE/RR AGG1 is established, one prefix is received.
We Display extra information about the prefix VPNv4 received which come with the Ext-Comm 7922:16 needed to import route in the VRF corresponding.
The prefix 172.16.2.0/30 comming from PE-OCNOS2 have been imported int the VRF DATA_OLT
IOS XR BGP configuration and verification
For this example (Lab) XR is working as CORE and RR which in real environment is not recommended.
router bgp 7922
nsr
bgp router-id 11.11.11.11
bgp graceful-restart
bgp log neighbor changes detail
address-family vpnv4 unicast
additional-paths receive
additional-paths send
!
session-group SG-iBGP
remote-as 7922
password encrypted 011608105E070D0A38
!
neighbor-group TO_OCNOS
use session-group SG-iBGP
update-source Loopback0
address-family vpnv4 unicast
route-reflector-client
next-hop-self
soft-reconfiguration inbound always
!
!
neighbor-group TO_RR_CORE
use session-group SG-iBGP
update-source Loopback0
address-family vpnv4 unicast
next-hop-self
soft-reconfiguration inbound
!
!
neighbor 2.2.2.2
use neighbor-group TO_RR_CORE
!
neighbor 11.11.11.111
use neighbor-group TO_OCNOS
!
!
BGP VPNv4 family is enabled to OcNOS PE1 and XR AGG2 which is the another RR.
From AGG1 XR we check two prefix in the family VPNv4 comming from OcNOS Routers.
EVPN-VPWS among PE-OcNOS
This section walks through how we mapped EVPN-VPWS services to achieve a stable point-to-point L2 service.
OcNOS EVPN-VPWS service setup and interface mapping
PE-OCNOS1
router bgp 7922
address-family l2vpn evpn
neighbor RR_CORE activate
exit-address-family
!
evpn mpls enable
!
mac vrf EVPN-VPWS
rd 11.11.11.111:7922
route-target both 7922:1
!
evpn mpls vtep-ip-global 11.11.11.111
!
evpn mpls id 102 xconnect target-mpls-id 101
host-reachability-protocol evpn-bgp EVPN-VPWS
!
interface eth3.100 switchport
access-if-evpn
map vpn-id 102
PE-OCNOS2
router
bgp 7922
address-family
l2vpn evpn
neighbor
RR_CORE activate
exit-address-family
!
evpn
mpls enable
!
!
mac
vrf EVPN-VPWS
rd 9.9.9.9:7922
route-target both 7922:1
!
evpn
mpls vtep-ip-global 9.9.9.9
!
evpn
mpls id 101 xconnect target-mpls-id 102
host-reachability-protocol evpn-bgp EVPN-VPWS
!
interface
eth3.100 switchport
access-if-evpn
map vpn-id 101
Verify by checking EVPN route-types, label allocation, and service status. Record the time the service becomes active and run traffic tests to confirm data-plane stability.
End-to-End EVPN-VPWS Validation: Address, Label, and Traffic Tests
EVPN VPWS status is UP (NW-SET)
Labels have been assigned to VPWS in this status express Resolved means control planel is ready.
These last displays shows BGP attributes related to EVPN VPWS like prefix EVPN Type 1 (Ethernet Route Discovery) Learnt from PE OcNOS 2 9.9.9.9